
Difference between Extrusion Blow Molding and Injection Blow Molding
Difference between Extrusion Blow Molding and Injection Blow Molding
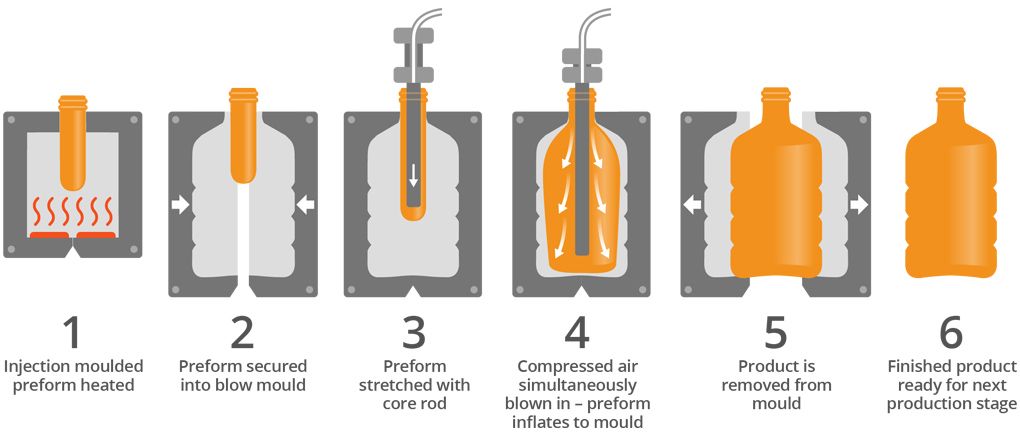
When manufacturing plastic containers, bottles, and various hollow plastic products, two widely used processes are extrusion blow molding and injection blow molding. These processes are the backbone of many industries, including packaging, automotive, and consumer goods. This comprehensive guide dives deep into the extrusion blow molding process and the injection blow molding machine, exploring their differences, advantages, and applications.
Understanding Extrusion Blow Molding
Extrusion Blow Molding Process Overview
Extrusion blow molding is a highly versatile manufacturing technique to create hollow plastic objects. The process involves extruding a parison, which is a hot, tubular plastic shape, and then blowing air into it to expand it into the desired shape within a mold cavity.
Critical Stages of Extrusion Blow Molding
Material Extrusion: The process starts with the plastic material, usually in pellets or granules, melting and forming into a continuous parison tube.
Parison Formation: The parison is clamped into a mold cavity with a blow pin positioned inside.
Blowing: Compressed air is injected into the parison, causing it to expand and conform to the shape of the mold cavity.
Cooling and Solidification: The plastic is cooled, solidifies, and takes the shape of the mold.
Ejection: The finished product is ejected from the mold, and the process is ready to start again.
Advantages of Extrusion Blow Molding
Cost-Efficient: It's a cost-effective method for producing large quantities of hollow plastic products.
Wide Range of Shapes: It can create various shapes and sizes, making it suitable for items like bottles, containers, and tanks.
Quick Production: Production speeds are relatively high compared to other molding processes.
Applications of Extrusion Blow Molding
Bottles and Containers: Extrusion blow molding is commonly used in the packaging industry for producing bottles, jugs, and containers.
Automotive Components: Some automotive parts, like air ducts and tanks, are manufactured using this process.
Toys and Sporting Goods: Hollow toys, balls, and sporting equipment are also created through extrusion blow molding.
Exploring Injection Blow Molding
Injection Blow Molding Machine: An Overview
Injection blow molding is another widely used technique for manufacturing hollow plastic products. It's distinct from extrusion blow molding in several vital ways.
Critical Stages of Injection Blow Molding
Injection: Unlike extrusion blow molding, injection blow molding starts with a preform created through injection molding. This preform is a partially formed plastic piece resembling the final product.
Blowing: The preform is transferred to a blow mold, inflating it using compressed air to take the shape of the mold cavity.
Cooling and Solidification: Cooling is crucial to maintain the product's shape.
Ejection: The finished product is ejected from the mold.
Advantages of Injection Blow Molding
Precise Control: Injection blow molding allows for precise control over wall thickness and intricate design features.
Excellent Finish: Products often have a smoother, more refined finish.
Minimal Material Waste: It generates less material waste than extrusion blow molding.
Applications of Injection Blow Molding
Pharmaceutical Packaging: Small bottles and vials for medicines.
Cosmetic Containers: High-quality packaging for cosmetics and perfumes.
Industrial Components: Some complex and small industrial components are made using injection blow molding.
Key Differences at a Glance
Process Origin
Extrusion Blow Molding: The process begins with creating a parison through extrusion.
Injection Blow Molding: It starts with forming a preform through injection molding.
Product Characteristics
Extrusion Blow Molding: Suited for more extensive, simpler shapes with thicker walls.
Injection Blow Molding: Ideal for smaller, intricate shapes with thinner walls.
Finish
Extrusion Blow Molding: This may result in a slightly rougher finish.
Injection Blow Molding: Offers a smoother and more refined finish.
Material Usage
Extrusion Blow Molding: Tends to use more material due to thicker walls.
Injection Blow Molding: Generally uses less material, reducing waste.
Production Speed
Extrusion Blow Molding: Often faster, making it suitable for high-volume production.
Injection Blow Molding: Slower than extrusion blow molding, making it better for smaller batches.
Conclusion
In plastic manufacturing, extrusion and injection blow molding have unique strengths and applications. Extrusion blow molding excels in producing larger, simpler shapes, making it ideal for high-volume production of items like bottles and containers. On the other hand, injection blow molding shines when it comes to creating smaller, more intricate products with a polished finish, often found in pharmaceutical and cosmetic packaging.
Choosing between these processes ultimately depends on the specific requirements of your product and your production goals. Understanding their differences is critical to making an informed decision and achieving the best results for your plastic manufacturing needs.
